Steps To Generate Api Key In Android
- When using the signed API key, the MapView will show up ONLY when the app is installed from the Android Market. So, installing the app from Eclipse (Run As, Debug As, etc) or command line (adb install) won't show the MapView. Rest assured, once the app is in the Market.
- Generating Google map Release API Key. Ask Question Asked 7 years. Before publishing application into play store you have to follow some step to create release key. Step 1: First find your key store location. If you cannot generate api key then you can use my key as given define.
To use the Google Awareness API, you must add a Google API key to your app. Thetype of API key you need is an Android API key.
In the left side, Api&Auth-Api.You have to turn on Google cloud messaging for android. For me,I have to Click Credentials in Api&Auth to create a key.Below I am shown a screenshot for that. Finally,Click create new key to generate a key for your application.see here for SHA-1 fingerprint.
All Android apps are signed with a digital certificate for which you hold theprivate key. For more information about digital certificates, refer to theAndroid guide on how tosign your app.
Android API keys are linked to specific certificate-package pairs. You onlyneed one key for each certificate, no matter how many users you have for theapp.
Several steps are required for you to get a key for your app. They're describedin detail in this guide, and are summarized as follows:
- Get information about your app's certificate.
- Register a project in the Google Developers console and add the User ContextAPI as a service for the project.
- Request a key.
- Add the key to your app. To do so, add an element to your app manifest.
Find your app's certificate information
The API key is based on a short form of your app's digital certificate, known as its SHA-1 fingerprint. To display the SHA-1 fingerprint for your certificate, first ensure that you use the right certificate. You might have the following two certificates to choose from:
- A debug certificate: The Android SDK tools generate this certificate automatically when you do a debug build. Only use this certificate with apps that you're testing. Don't attempt to publish an app that's signed with a debug certificate. The debug certificate is described in more detail in the Sign your debug build section in the Android developer documentation.
- A release certificate: The Android SDK tools generate this certificate when you do a release build. You can also generate this certificate with the
keytoolprogram. Use this certificate when you're ready to release your app to the world.
For more information about keytool, see its Oracle documentation.
Display the debug certificate fingerprint
Use the keytool program with the -v parameter to display a certificate's SHA-1 fingerprint. To do so, complete the following steps:
Locate your debug keystore file. The file name is
debug.keystore, and it's created the first time you build your project. By default, it's stored in the same directory as your Android Virtual Device (AVD) files:- OS X and Linux:
~/.android/ - Windows Vista and Windows 7:
C:Usersyour_user_name.android
- OS X and Linux:
List the SHA-1 fingerprint:
For Linux or OS X, open a terminal window and enter the following:
/norton-license-key-generator-free-download.html. For Windows Vista and Windows 7, run the following:
You should see output similar to the following:
-->To use the Google Maps functionality in Android, you need toregister for a Maps API key with Google. Until you do this, you willjust see a blank grid instead of a map in your applications. You mustobtain a Google Maps Android API v2 key - keys from the older GoogleMaps Android API key v1 will not work.
Obtaining a Maps API v2 key involves the following steps:
- Retrieve the SHA-1 fingerprint of the keystore that is used to sign the application.
- Create a project in the Google APIs console.
- Obtaining the API key.
Obtaining your Signing Key Fingerprint
To request a Maps API key from Google, you need to know theSHA-1 fingerprint of the keystore that is used to sign the application.Typically, this means you will have to determine the SHA-1 fingerprintfor the debug keystore, and then the SHA-1 fingerprint for the keystorethat is used to sign your application for release.
By default the keystore that is used to sign debug versions of aXamarin.Android application can be found at the following location:
C:Users[USERNAME]AppDataLocalXamarinMono for Androiddebug.keystore
Information about a keystore is obtained by running the keytoolcommand from the JDK. This tool is typically found in the Java bindirectory:
C:Program FilesAndroidjdkmicrosoft_dist_openjdk_[VERSION]binkeytool.exe
By default the keystore that is used to sign debug versions of aXamarin.Android application can be found at the following location:
/Users/[USERNAME]/.local/share/Xamarin/Mono for Android/debug.keystore
Information about a keystore is obtained by running the keytoolcommand from the JDK. This tool is typically found in the Java bindirectory:
/System/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/[VERSION].jdk/Contents/Home/bin/keytool
Run keytool using the following command (using the file paths shownabove):
Debug.keystore Example
For the default debug key (which is automatically created for you fordebugging), use this command:
Production Keys
When deploying an app to Google Play, it must besigned with a private key.The keytool will need to be run with the private key details, and theresulting SHA-1 fingerprint used to create a production Google Maps APIkey. Remember to update the AndroidManifest.xml file with thecorrect Google Maps API key before deployment.
Keytool Output
You should see something like the following output in your consolewindow:
You will use the SHA-1 fingerprint (listed after SHA1) later in this guide.
Creating an API project
After you have retrieved the SHA-1 fingerprint of the signing keystore, it is necessary to create a new project in the Google APIs console (or add the Google Maps Android API v2 service to an existing project).
Generate Api Key For Google Maps
In a browser, navigate to the Google Developers Console API & Services Dashboard and click Select a project. Click on a project name or create a new one by clicking NEW PROJECT:
If you created a new project, enter the project name in the New Project dialog that is displayed. This dialog will manufacture a unique project ID that is based on your project name. Next, click the Create button as shown in this example:
After a minute or so, the project is created and you are taken to the Dashboard page of the project. From there, click ENABLE APIS AND SERVICES:
From the API Library page, click Maps SDK for Android. On the next page, click ENABLEto turn on the service for this project:
At this point the API project has been created and Google Maps Android API v2 has been added to it. However, you cannot use this API in your project until you create credentials for it. The next section explains how to create an API key and white-list a Xamarin.Android application so that it is authorized to use this key.
Obtaining the API Key
After the Google Developer Console API project has been created, it is necessary to create an Android API key. Xamarin.Android applications must have an API key before they are granted access to Android Map API v2.
In the Maps SDK for Android page that is displayed (after clicking ENABLE in the previous step), go to the Credentials tab and click the Create credentials button:
Click API key:
After this button is clicked, the API key is generated. Next it is necessary to restrict this key so that only your app can call APIs with this key. Click RESTRICT KEY:
Change the Name field from API Key 1 to a name that will help you remember what the key is used for (XamarinMapsDemoKey is used in this example). Next, click the Android apps radio button:
To add the SHA-1 fingerprint, click + Add package name and fingerprint:
Enter your app's package name and enter the SHA-1 certificate fingerprint (obtained via
keytoolas explained earlier in this guide). In the following example, the package name forXamarinMapsDemois entered, followed by the SHA-1 certificate fingerprint obtained from debug.keystore:Note that, in order for your APK to access Google Maps, you must include SHA-1 fingerprints and package names for every keystore (debug and release) that you use to sign your APK. For example, if you use one computer for debug and another computer for generating the release APK, you should include the SHA-1 certificate fingerprint from the debug keystore of the first computer and the SHA-1 certificate fingerprint from the release keystore of the second computer. Click + Add package name and fingerprint to add another fingerprint and package name as shown in this example:
Click the Save button to save your changes. Next, you are returned to the list of your API keys. If you have other API keys that you have created earlier, they will also be listed here. In this example, only one API key (created in the previous steps) is listed:
Connect the project to a billable account
Beginning June,11 2018, the API key will not work if the project is not connected to a billable account (even if the service is still free for mobile apps).
Click the hamburger menu button and select the Billing page:
Link the project to a billing account by clicking Link a billing account followed by CREATE BILLING ACCOUNT on the displayed popup (if you don't have an account, you will be guided to create a new one):
Adding the Key to Your Project
Free Api Key
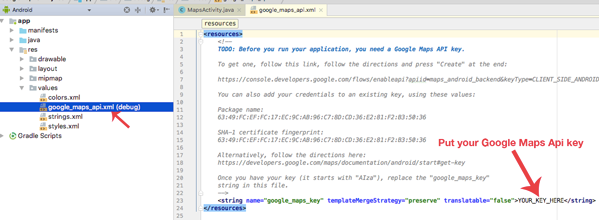
Google Api Key

Finally, add this API key to the AndroidManifest.XML file of your Xamarin.Android app. In the following example, YOUR_API_KEY is to be replaced with the API key generated in the previous steps: